Why is ergothioneine good for the brain?
In the quest for optimal brain health and cognitive function, researchers have uncovered a powerful ally: ergothioneine. This unique amino acid, found naturally in mushrooms and some other foods, has garnered significant attention for its potential neuroprotective properties. As we delve into the world of brain health, let's explore why ergothioneine is emerging as a promising compound for maintaining and enhancing cognitive function.

How ergothioneine protects brain cells?
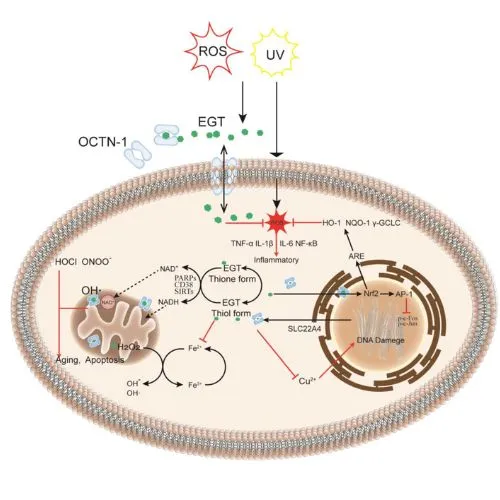
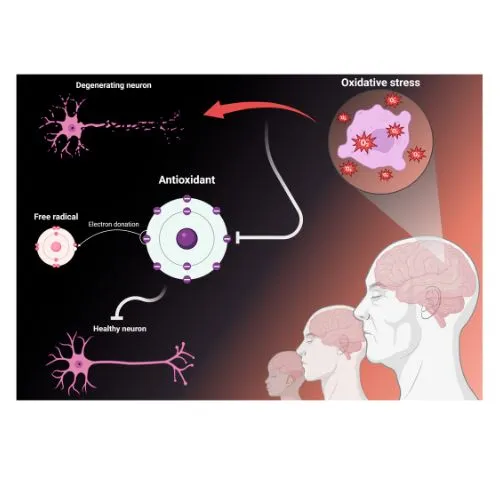
Ergothioneine's role in protecting brain cells is multifaceted and impressive. This potent antioxidant works tirelessly to shield neurons from oxidative stress, a major contributor to brain aging and neurodegenerative diseases.
Antioxidant properties of ergothioneine
At its core, ergothioneine is a powerhouse antioxidant. It neutralizes harmful free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can damage cellular components, including DNA, proteins, and lipids. This antioxidant action is particularly crucial in the brain, where oxidative stress can lead to neuronal death and cognitive decline.
What sets ergothioneine apart from other antioxidants is its unique chemical structure. It contains a 2-thiol-imidazole moiety that allows it to exist in a tautomeric form, enhancing its stability and antioxidant capacity. This structural advantage enables product to maintain its protective effects for extended periods, providing long-lasting defense against oxidative damage in brain cells.
Mitochondrial support
Ergothioneine doesn't just combat free radicals; it also supports the powerhouses of our cells - the mitochondria. In brain cells, mitochondria are crucial for energy production and overall cellular health. It has been shown to accumulate in mitochondria, where it helps maintain mitochondrial function and integrity.
By supporting mitochondrial health, ergothioneine ensures that brain cells have the energy they need to function optimally. This is particularly important in neurons, which have high energy demands due to their constant signaling activities.
Metal ion chelation
Another way ergothioneine protects brain cells is through its metal ion chelation properties. Excess metal ions, such as iron and copper, can catalyze the production of harmful free radicals in the brain. Ergothioneine can bind to these metal ions, reducing their ability to generate oxidative stress.
This chelation ability is especially relevant in the context of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, where metal ion imbalances are often observed. By helping to maintain proper metal ion homeostasis, it contributes to a healthier brain environment.
Neuroprotective benefits of ergothioneine
Beyond its general protective effects, ergothioneine offers specific neuroprotective benefits that make it a promising compound for brain health.
Reduction of neuroinflammation
Chronic inflammation in the brain, or neuroinflammation, is a common factor in various neurodegenerative disorders. Ergothioneine has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties that could help mitigate this damaging process.
Studies have shown that ergothioneine can modulate inflammatory pathways, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibiting the activation of inflammatory cells in the brain. This anti-inflammatory action may help prevent or slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases associated with chronic inflammation.
Protection against neurotoxins
Ergothioneine has shown promise in protecting neurons from various neurotoxins. In experimental models, it has demonstrated the ability to reduce the harmful effects of substances like beta-amyloid (associated with Alzheimer's disease) and 6-hydroxydopamine (used to model Parkinson's disease).
This protective effect is likely due to a combination of ergothioneine's antioxidant properties and its ability to maintain cellular energy metabolism. By shielding neurons from these toxic insults, it may help preserve brain function and slow the progression of neurodegenerative processes.
Enhanced cellular stress response
Ergothioneine doesn't just passively protect brain cells; it also enhances their ability to respond to stress. Research has shown that ergothioneine can activate cellular stress response pathways, including the Nrf2 pathway, which is responsible for turning on genes that produce antioxidant enzymes.
By boosting the brain's own defense mechanisms, ergothioneine helps create a more resilient neural environment. This adaptive response could be particularly beneficial in protecting against age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
Ergothioneine and cognitive health support
The neuroprotective properties of ergothioneine translate into tangible benefits for cognitive health and function. As research in this area continues to grow, several key areas of cognitive support have emerged.
Memory enhancement
One of the most exciting potential benefits of ergothioneine is its impact on memory. Studies have shown a correlation between higher blood levels of ergothioneine and better memory performance in older adults.
The mechanism behind this memory-enhancing effect likely involves ergothioneine's ability to protect neurons involved in memory formation and retrieval. By maintaining the health of these critical brain cells, it may help preserve memory function as we age.
Improved executive function
Executive function, which includes skills like planning, decision-making, and multitasking, is another area where ergothioneine shows promise. Research has indicated that individuals with higher ergothioneine levels tend to perform better on tests of executive function.
This improvement in executive function could be attributed to ergothioneine's protective effects on the prefrontal cortex, a brain region crucial for these higher-order cognitive processes. By supporting the health of this region, ergothioneine may help maintain and even enhance executive function abilities.
Potential in neurodegenerative disease prevention
While more research is needed, early studies suggest that ergothioneine could play a role in preventing or slowing the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
The compound's ability to combat oxidative stress, reduce inflammation, and protect against neurotoxins makes it a promising candidate for neuroprotection. Some studies have found lower levels of ergothioneine in individuals with these conditions, suggesting that maintaining adequate levels could be protective.
Cognitive longevity
As we age, maintaining cognitive function becomes increasingly important. Ergothioneine's multifaceted approach to brain protection – from antioxidant action to mitochondrial support – positions it as a potential ally in the pursuit of cognitive longevity.
By helping to preserve brain health and function over time, ergothioneine could contribute to maintaining cognitive abilities well into our later years. This potential for supporting healthy brain aging makes product an intriguing subject for further research in the field of cognitive health.
Conclusion
The growing body of research on ergothioneine paints a promising picture of its potential benefits for brain health. From its potent antioxidant properties to its neuroprotective effects and cognitive support, it stands out as a compound of significant interest in the field of neuroscience and cognitive health.
As we continue to unravel the complexities of brain health and aging, ergothioneine emerges as a valuable ally in our quest for cognitive longevity. Its unique properties and wide-ranging effects on brain function make it a compound worth considering for those looking to support their brain health naturally.
For more information about ergothioneine and its potential benefits, please contact us at info@yanggebiotech.com. Our team of experts is ready to answer your questions and provide you with high-quality products to support your brain health goals.
References
1. Halliwell, B., Cheah, I. K., & Tang, R. M. Y. (2018). Ergothioneine - a diet-derived antioxidant with therapeutic potential. FEBS Letters, 592(20), 3357-3366.
2. Cheah, I. K., & Halliwell, B. (2012). Ergothioneine; antioxidant potential, physiological function and role in disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease, 1822(5), 784-793.
3. Beelman, R. B., Kalaras, M. D., & Richie, J. P. (2019). Micronutrients and Bioactive Compounds in Mushrooms: A Recipe for Healthy Aging? Nutrients, 11(9), 1948.
4. Nakamichi, N., Kato, Y., Ishitsu, T., & Tamai, I. (2013). Ergothioneine is a novel neuroprotective compound against oxidative stress-induced neuronal cell death. Neuroscience Letters, 549, 129-132.
5. Cheah, I. K., Feng, L., Tang, R. M. Y., Lim, K. H. C., & Halliwell, B. (2016). Ergothioneine levels in an elderly population decrease with age and incidence of cognitive decline; a risk factor for neurodegeneration? Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 478(1), 162-167.

Based on your location and order quantity, you will have the opportunity to receive a limited time free shipping promotion!

Who we are


