What is the difference between lutein and zeaxanthin?
Lutein and zeaxanthin are two powerful carotenoids that play crucial roles in maintaining eye health and supporting overall well-being. While these compounds share many similarities, they also have distinct characteristics and functions. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the differences between lutein and zeaxanthin, their unique benefits, and how they work together to protect your vision.

Role of Lutein in Supporting Eye Health
Lutein as a Macular Pigment
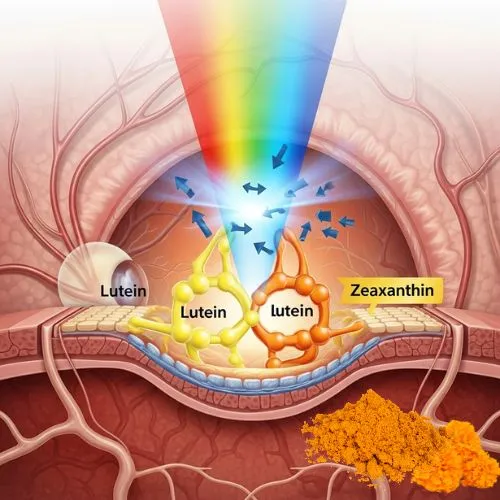
Lutein is a xanthophyll carotenoid that accumulates in the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision. As a key component of macular pigment, it acts as a natural sunscreen for the eyes, filtering out harmful blue light and protecting the delicate photoreceptor cells from oxidative damage. This protective function is crucial in maintaining long-term eye health and preventing age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Antioxidant Properties of Lutein
Beyond its role as a light filter, lutein exhibits potent antioxidant properties. It neutralizes free radicals and reactive oxygen species that can damage cellular structures within the eye. This antioxidant activity helps to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which are key factors in the development of various eye diseases, including cataracts and diabetic retinopathy.
Lutein and Visual Performance
Research has shown that higher levels of lutein in the macula correlate with improved visual performance. This includes enhanced contrast sensitivity, reduced glare sensitivity, and better visual acuity under low-light conditions. These benefits are particularly important for older adults and individuals who spend long hours looking at digital screens, as it can help alleviate eye strain and fatigue associated with prolonged screen time.

Lutein vs Zeaxanthin: Functions and Food Sources
Structural Differences
Lutein and zeaxanthin are xanthophyll carotenoids with similar yet distinct molecular structures. It contains a hydroxyl group on each end of its molecule, while zeaxanthin differs by having an extra double bond in its central chain. Though subtle, this variation influences their spatial arrangement and bioavailability, affecting how each compound is absorbed, distributed, and utilized within the eye and other body tissues for protective and functional roles.
Distribution in the Eye
Lutein and zeaxanthin are distributed differently within the eye, reflecting their specialized functions. Lutein is predominantly found in the peripheral retina and is closely linked to rod photoreceptor cells, which support vision in dim light. In contrast, zeaxanthin is highly concentrated in the central macula, where it plays a vital role in protecting and supporting cone photoreceptor cells. These cones are essential for color perception and sharp visual acuity, making zeaxanthin crucial for detailed, high-resolution vision.
Dietary Sources
Both lutein and zeaxanthin are found in various foods, but their relative concentrations can differ. Lutein is particularly abundant in green leafy vegetables such as spinach, kale, and collard greens. It's also found in notable quantities in brussels sprouts, broccoli, and zucchini. Zeaxanthin, while present in many of the same foods, is found in higher concentrations in orange and yellow fruits and vegetables, including corn, orange peppers, and mandarin oranges. Egg yolks are an excellent source of both lutein and zeaxanthin, with the added benefit of high bioavailability due to the presence of dietary fats.

How Lutein Works Together with Zeaxanthin?
Synergistic Protection
Lutein and zeaxanthin work synergistically to protect the eyes from oxidative damage and harmful light exposure. Their complementary distribution within the retina allows for comprehensive protection across different regions of the eye. Together, they form a powerful antioxidant network that scavenges free radicals, reduces inflammation, and maintains the structural integrity of ocular tissues.
Blue Light Filtration
One of the most important functions of lutein and zeaxanthin is their ability to filter out high-energy blue light. This type of light, which is emitted by digital devices and LED lighting, can penetrate deep into the eye and cause photochemical damage to the retina. Lutein and zeaxanthin absorb different wavelengths of blue light, providing a more complete protective shield against this potential threat to eye health.
Cognitive Benefits
Recent research has uncovered potential cognitive benefits associated with lutein and zeaxanthin consumption. These carotenoids accumulate in brain tissue, particularly in areas associated with memory and information processing. Studies have suggested that higher levels of lutein and zeaxanthin in the brain may be linked to improved cognitive function, especially in older adults. This emerging area of research highlights the importance of these nutrients beyond just eye health.
Conclusion
Lutein and zeaxanthin are indispensable partners in maintaining optimal eye health and visual function. While they share many similarities, their subtle differences in structure and distribution allow them to provide comprehensive protection throughout the eye. By understanding the unique roles of these carotenoids, we can appreciate the importance of incorporating lutein and zeaxanthin-rich foods into our diets or considering supplementation to support long-term eye health and overall well-being.
At Yangge Biotech Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-quality natural plant extracts, including lutein derived from marigold flowers. Our marigold extract lutein powder is available in concentrations ranging from 5% to 80%, ensuring you have access to this vital nutrient in the form that best suits your needs. As a leading supplier of botanical ingredients, we are committed to providing innovative solutions for the food, beverage, and dietary supplement industries. To learn more about our lutein products or other natural plant extracts, please contact us at info@yanggebiotech.com.
FAQ
Q: Can we get some samples to test before purchasing?
A: Of course, we can provide free samples of 20 to 100 grams, but the shipping cost is at the customer's expense. The shipping cost can be deducted from the next order, or the samples can be sent through your courier account.
Q: Do your products have relevant certifications?
A: Yes, our products are certified for HALAL, ISO, HACCP, Kosher, and other certifications.
Q: What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ)?
A: Small batches of samples can be customized according to your requirements.
Q: Do you offer OEM and ODM services? Can the formula be customized based on our own?
A: Of course, we provide ODM and OEM services to many customers. Our product range includes softgels, capsules, tablets, sachets, granules, and private label services. Simply contact us and let us know your requirements. Our experienced R&D team can also develop new products with specific formulas.
Please contact us to design your own branded products.
Q: How do you handle quality complaints?
A: First, we have a comprehensive quality control SOP. We provide authoritative third-party inspection reports for almost all products before shipment to minimize the possibility of quality issues. Second, we have a comprehensive return and exchange procedure. If there is a genuine quality dispute, we will strictly follow the SOP.
Q: How do you ship? How long does delivery take?
A: For small orders, we typically use DHL, UPS, EMS, FedEx, or TNT. Delivery typically takes 3-7 days. We also offer air and sea freight services. We have a strong freight forwarding team and can provide you with a one-stop service, including DDP and DDU.
Q: What are your payment terms?
A: 100% prepayment, payable by T/T, Western Union, MoneyGram, or PayPal.
Q: What is the shelf life of your products?
A: 2 years with proper storage.
Q: Is the packaging environmentally friendly?
A: We attach great importance to environmental protection and are constantly improving our product packaging. Some products are packaged in recyclable paper. Packaging materials are carefully selected to ensure product safety during transportation and storage, and to minimize environmental impact. We are committed to achieving a balance between environmental friendliness and practicality in our product packaging, and to contributing to sustainable development.
References
1. Bernstein, P. S., et al. (2016). Lutein, zeaxanthin, and meso-zeaxanthin: The basic and clinical science underlying carotenoid-based nutritional interventions against ocular disease. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research, 50, 34-66.
2. Mares, J. (2016). Lutein and zeaxanthin isomers in eye health and disease. Annual Review of Nutrition, 36, 571-602.
3. Stringham, J. M., et al. (2019). Macular carotenoid supplementation improves visual performance, sleep quality, and adverse physical symptoms in those with high screen time exposure. Foods, 8(7), 213.
4. Johnson, E. J. (2014). Role of lutein and zeaxanthin in visual and cognitive function throughout the lifespan. Nutrition Reviews, 72(9), 605-612.
5. Eisenhauer, B., et al. (2017). Lutein and zeaxanthin—food sources, bioavailability and dietary variety in age-related macular degeneration protection. Nutrients, 9(2), 120.

Based on your location and order quantity, you will have the opportunity to receive a limited time free shipping promotion!

Who we are


