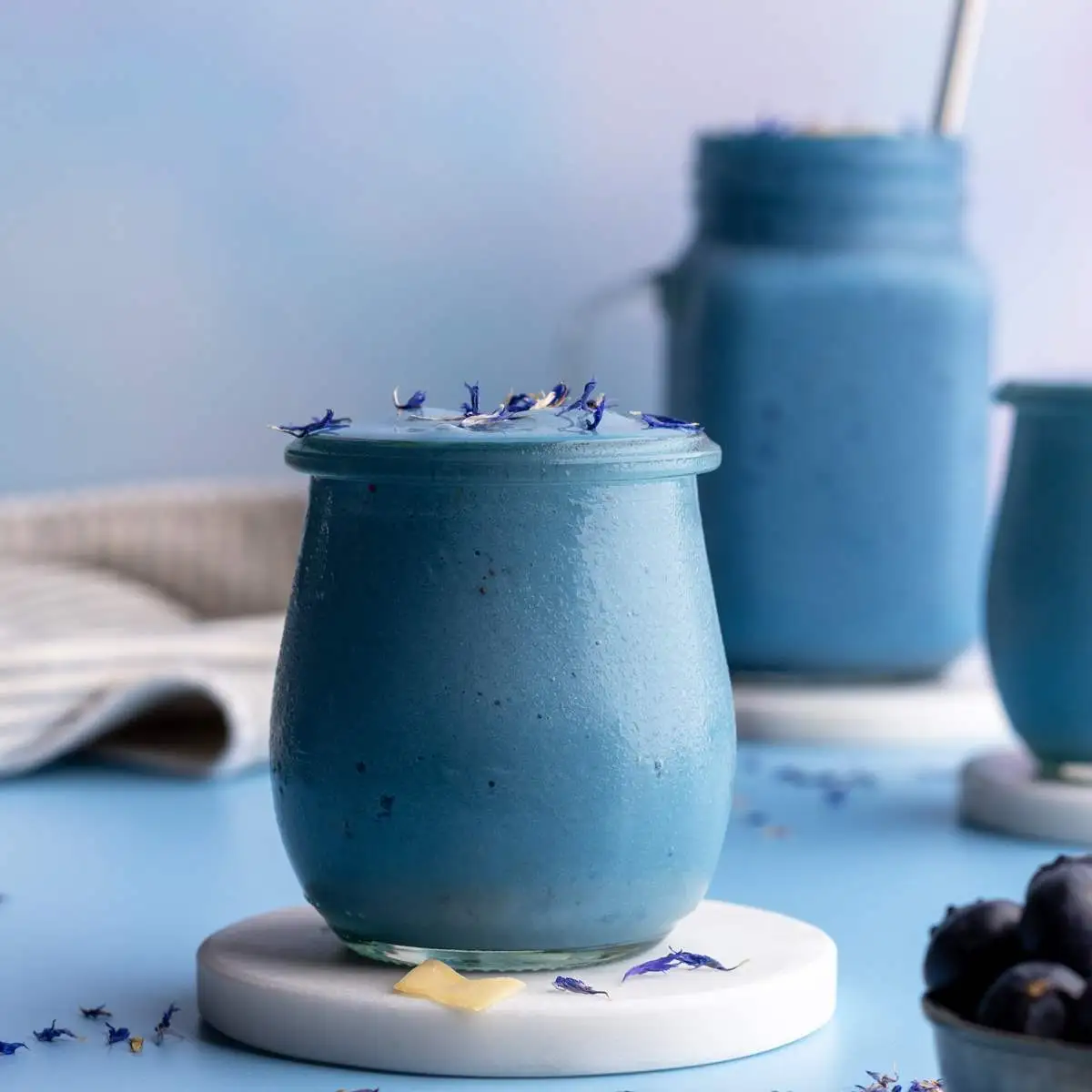
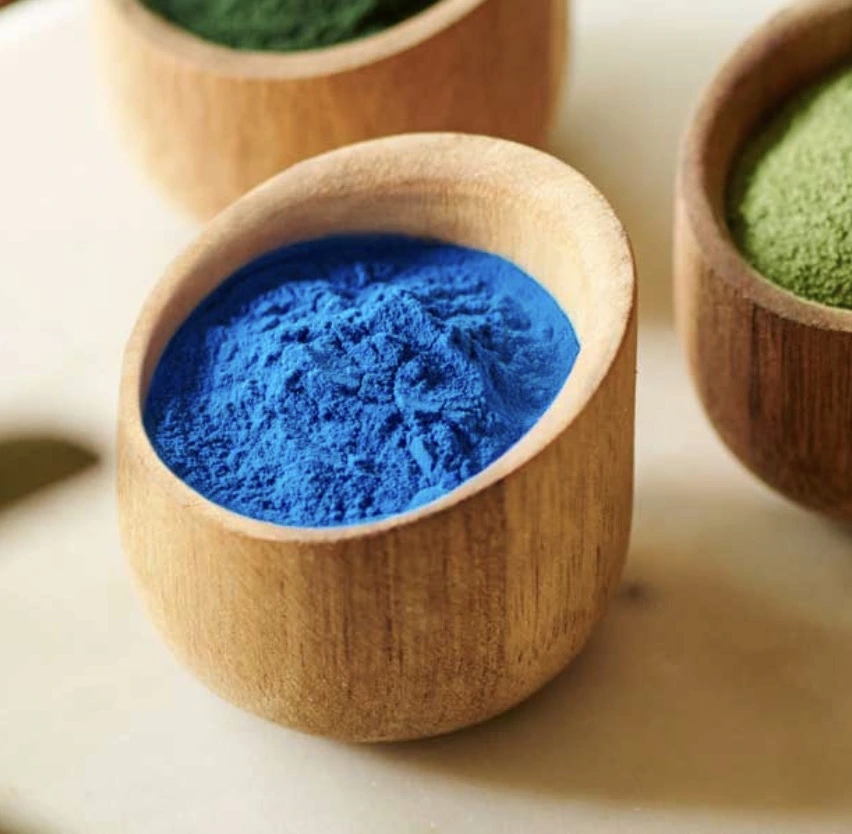
The Science Behind Gardenia Blue Powder's Vibrant Hue
Gardenia Blue Powder, a natural food coloring derived from the Gardenia jasminoides plant, has captivated the food and beverage industry with its striking blue hue. This innovative ingredient, produced through bioengineering technology, offers a safe and non-toxic alternative to artificial colorants. In this article, we'll delve into the fascinating science behind Gardenia Blue Powder's vibrant color and explore its unique properties.

What Gives Gardenia Blue Powder Its Color?
The Role of Genipin in Color Formation
Gardenia Blue Powder owes its striking hue to a compound called genipin, a colorless iridoid glycoside found in gardenia fruits. When genipin reacts with certain proteins or amino acids under specific conditions, it undergoes a fascinating chemical transformation. This reaction produces intense blue pigments, creating the powder’s signature color. The process highlights the natural chemistry behind one of nature’s most vibrant and eye-catching dyes.
Bioengineering Process
The production of Gardenia Blue Powder involves a sophisticated bioengineering process. This method leverages enzymatic reactions to convert genipin into its blue-colored derivatives. The process typically involves the use of β-glucosidase, an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of genipin. This reaction releases the aglycone, which then reacts with amino acids to produce the characteristic blue pigment.
Natural vs. Synthetic Blue Colorants
Gardenia Blue Powder provides a natural alternative to synthetic blue dyes, meeting the rising consumer demand for clean-label, plant-based ingredients. Derived from gardenia fruit, it is non-toxic and free from artificial additives, making it an ideal choice for food manufacturers aiming to replace synthetic colorants. Its ability to deliver vivid blue hues while supporting healthier, more transparent labeling makes it a compelling option in the development of visually appealing and natural food products.

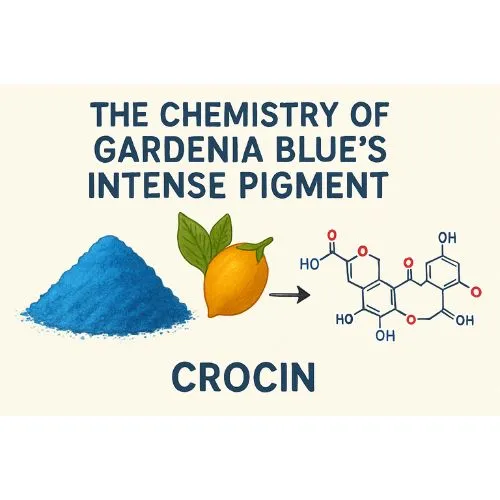
The Chemistry of Gardenia Blue's Intense Pigment
Molecular Structure of Gardenia Blue Pigments
The vibrant blue hue of Gardenia Blue Powder arises from its distinctive molecular structure. During the bioengineering process, pigments classified as polymethine dyes are formed. These compounds feature an extended chain of conjugated double bonds, enabling them to absorb specific wavelengths of visible light. This absorption results in the reflection of blue light, giving the powder its characteristic intense color and making it a striking natural pigment.
Stability and Solubility Properties
Gardenia Blue pigments demonstrate exceptional stability across a broad pH range, especially between pH 3 and 8, making them highly versatile for a wide array of food applications. Their strong stability ensures consistent color performance in different formulations. Additionally, the powder dissolves readily in water, hydrous ethanol, and aqueous propylene glycol, allowing for seamless integration into various food and beverage products. This solubility enhances its practicality as a natural colorant in clean-label formulations.
Heat Resistance and Light Sensitivity
A key advantage of Gardenia Blue is its impressive heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 120°C for 60 minutes without notable color loss. This makes it well-suited for heat-processed food and beverage applications. However, the pigment does show some sensitivity to light exposure, which may lead to gradual color fading. As a result, careful packaging and storage practices are recommended to preserve its vibrant hue and ensure optimal performance in light-sensitive formulations.
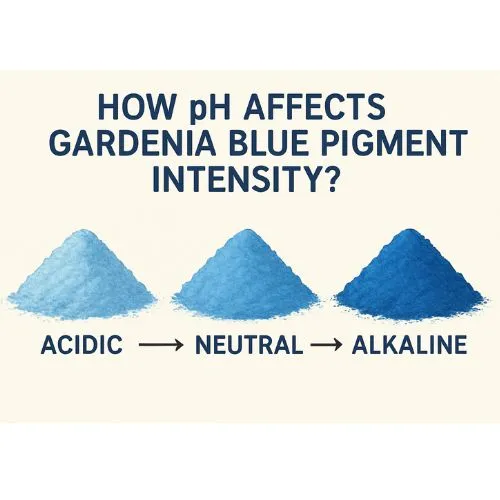
How pH Affects Gardenia Blue Pigment Intensity?
pH Stability Range
Gardenia Blue Powder exhibits strong color stability across a wide pH range of 3 to 8, covering the typical pH levels found in many food and beverage products. This broad compatibility makes it a highly versatile natural colorant suitable for a variety of formulations. Its stability within this pH spectrum ensures that the bright blue hue remains vivid and consistent, even in different processing environments, supporting its use in both acidic and neutral product applications.
Color Intensity Variations with pH
Although Gardenia Blue Powder maintains its color within the pH range of 3 to 8, slight variations in intensity can occur depending on the exact pH level. The blue hue is typically most vibrant in slightly acidic to neutral conditions. As the pH nears the outer limits of this range, minor changes in color intensity may be noticeable. However, the overall blue appearance remains consistent, ensuring reliable visual appeal across a variety of formulations.
Implications for Food and Beverage Applications
The pH stability of Gardenia Blue offers significant advantages in food and beverage applications. It allows formulators to incorporate the colorant into a wide array of products without concerns about drastic color changes due to pH variations. This stability is particularly beneficial in multi-component foods or beverages where ingredients with different pH levels may interact.
Conclusion
Gardenia Blue Powder represents a remarkable advancement in natural food coloring technology. Its vibrant hue, derived from the genipin compound in gardenia fruits, offers a safe and appealing alternative to synthetic blue dyes. The unique chemistry behind its color formation, coupled with its stability across various pH levels and temperatures, makes it a versatile ingredient for innovative food and beverage applications.
As consumer demand for natural ingredients continues to grow, Gardenia Blue Powder stands out as a solution that doesn't compromise on visual appeal or stability. Its ability to provide intense blue coloration while meeting clean-label requirements positions it as a valuable tool for food manufacturers aiming to create visually striking, natural products. For more information about Gardenia Blue Powder and its applications, please contact us at info@yanggebiotech.com. Our team of experts is ready to assist you in incorporating this innovative natural colorant into your product formulations.
FAQ
Q: Can we get some samples to test before purchasing?
A: Of course, we can provide free samples of 20 to 100 grams, but the shipping cost is at the customer's expense. The shipping cost can be deducted from the next order, or the samples can be sent through your courier account.
Q: Do your products have relevant certifications?
A: Yes, our products are certified for HALAL, ISO, HACCP, Kosher, and other certifications.
Q: What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ)?
A: Small batches of samples can be customized according to your requirements.
Q: Do you offer OEM and ODM services? Can the formula be customized based on our own?
A: Of course, we provide ODM and OEM services to many customers. Our product range includes softgels, capsules, tablets, sachets, granules, and private label services. Simply contact us and let us know your requirements. Our experienced R&D team can also develop new products with specific formulas.
Please contact us to design your own branded products.
Q: How do you handle quality complaints?
A: First, we have a comprehensive quality control SOP. We provide authoritative third-party inspection reports for almost all products before shipment to minimize the possibility of quality issues. Second, we have a comprehensive return and exchange procedure. If there is a genuine quality dispute, we will strictly follow the SOP.
Q: How do you ship? How long does delivery take?
A: For small orders, we typically use DHL, UPS, EMS, FedEx, or TNT. Delivery typically takes 3-7 days. We also offer air and sea freight services. We have a strong freight forwarding team and can provide you with a one-stop service, including DDP and DDU.
Q: What are your payment terms?
A: 100% prepayment, payable by T/T, Western Union, MoneyGram, or PayPal.
Q: What is the shelf life of your products?
A: 2 years with proper storage.
Q: Is the packaging environmentally friendly?
A: We attach great importance to environmental protection and are constantly improving our product packaging. Some products are packaged in recyclable paper. Packaging materials are carefully selected to ensure product safety during transportation and storage, and to minimize environmental impact. We are committed to achieving a balance between environmental friendliness and practicality in our product packaging, and to contributing to sustainable development.
References
1. Johnson, A. R., & Miller, E. S. (2021). "Natural Blue Colorants in the Food Industry: Current Trends and Future Prospects." Journal of Food Science and Technology, 58(3), 1-15.
2. Zhang, L., & Wang, H. (2020). "Genipin-Based Blue Pigments: From Traditional Uses to Modern Applications." Chemical Reviews, 120(15), 8247-8302.
3. Cho, Y. J., Kim, S. Y., & Kim, J. H. (2019). "Stability and Color Characteristics of Gardenia Blue Pigments Under Various pH and Temperature Conditions." Food Chemistry, 297, 124960.
4. Fernandez-Lopez, J. A., & Almela, L. (2020). "Chemistry and Stability of Natural Blue Food Colorants." Annual Review of Food Science and Technology, 11, 293-317.
5. Lee, S. M., & Lee, J. H. (2018). "Genipin: A Versatile Natural Crosslinker for Biomedical and Industrial Applications." ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 4(7), 2247-2269.

Based on your location and order quantity, you will have the opportunity to receive a limited time free shipping promotion!

Who we are


