The Connection Between Glutathione and Healthy Lung Function
Glutathione, often referred to as the body's master antioxidant, plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health. Its importance extends to lung function, where it acts as a powerful defender against oxidative stress and inflammation. This article explores the intricate relationship between glutathione and respiratory health, shedding light on how this remarkable compound contributes to maintaining and potentially improving lung function.

How Glutathione Boosts Lung Health and Respiratory Function?
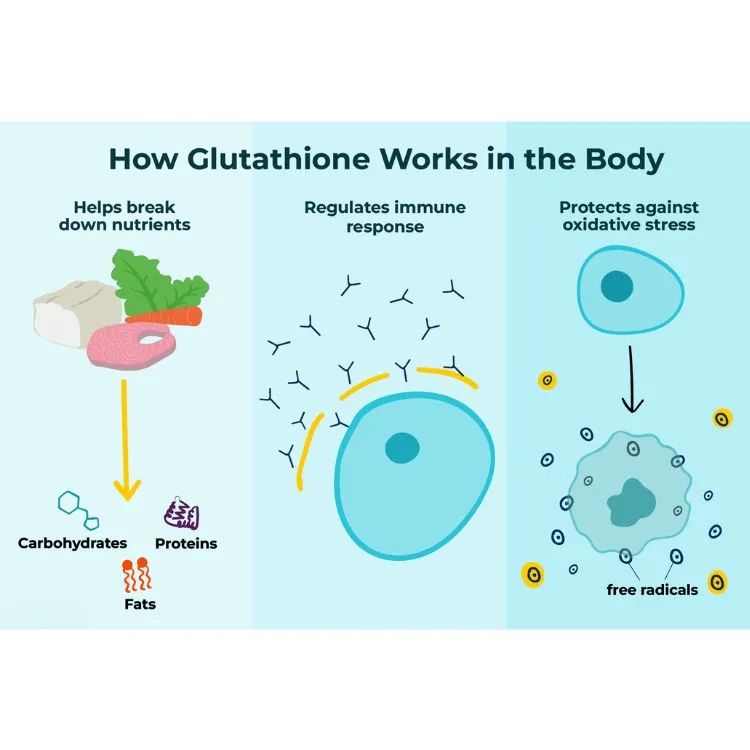
Glutathione's impact on lung health is multifaceted and profound. As a potent antioxidant, it helps neutralize harmful free radicals that can damage lung tissue. This protective action is particularly vital in the lungs, which are constantly exposed to environmental toxins and oxidative stress.
One of the primary ways glutathione supports respiratory function is by maintaining the integrity of the epithelial lining fluid (ELF) in the lungs. The ELF acts as a barrier against pathogens and irritants, and it helps keep this protective layer intact. Studies have shown that individuals with chronic respiratory conditions often have lower levels of glutathione in their ELF, suggesting a correlation between glutathione deficiency and compromised lung function.
Glutathione also plays a role in modulating the immune response within the lungs. It helps regulate inflammatory processes, which is crucial for preventing excessive inflammation that can lead to tissue damage. By maintaining a balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses, it contributes to optimal lung function and resilience against respiratory challenges.
Furthermore, glutathione aids in the detoxification of harmful substances that may enter the lungs. It facilitates the removal of toxins and heavy metals, helping to prevent accumulation that could otherwise lead to lung damage over time. This detoxifying action is particularly beneficial for individuals living in polluted environments or those exposed to occupational lung hazards.
Top Benefits of Glutathione for Preventing Lung Diseases
The role of glutathione in preventing lung diseases is becoming increasingly recognized in the medical community. Here are some of the top benefits associated with maintaining adequate glutathione levels for lung health:
- Protection against oxidative stress: Glutathione acts as a powerful antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals that can cause cellular damage in the lungs. This protection is crucial in preventing the development and progression of various lung diseases.
- Reduction of inflammation: Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of many respiratory conditions. Glutathione helps modulate the inflammatory response, potentially reducing the risk of inflammatory lung diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Enhanced mucociliary clearance: L-Glutathione supports the proper functioning of cilia, the tiny hair-like structures in the airways responsible for clearing mucus and debris. Improved mucociliary clearance can help prevent respiratory infections and maintain clear airways.
- Mitigation of environmental toxin effects: By aiding in the detoxification process, it helps protect lung tissue from damage caused by environmental pollutants, cigarette smoke, and other harmful substances.
- Preservation of lung elasticity: It may help maintain the elasticity of lung tissue, which is essential for efficient breathing and overall lung function. This benefit is particularly important as we age, as lung elasticity naturally decreases over time.
Is Glutathione Supplementation Key to Lung Function Recovery?
The potential of glutathione supplementation in supporting lung function recovery has garnered significant attention in recent years. While the body naturally produces glutathione, levels can become depleted due to various factors such as age, stress, poor diet, and certain health conditions. This has led researchers to investigate whether supplementation could be beneficial, particularly for individuals with compromised lung function.
Several studies have explored the effects of glutathione supplementation on lung health. Some research suggests that inhaled glutathione may help improve lung function in individuals with cystic fibrosis, a genetic disorder that affects the lungs and other organs. Other studies have investigated its potential benefits for patients with COPD, showing promising results in terms of improved respiratory symptoms and quality of life.
However, it's important to note that the efficacy of L-Glutathione supplementation can vary depending on the method of administration and the specific condition being addressed. Oral supplementation, for instance, may have limited bioavailability due to breakdown in the digestive system. Alternative methods such as inhalation or intravenous administration are being studied for their potential to deliver glutathione more effectively to the lungs.
While the research is encouraging, it's crucial to approach glutathione supplementation with caution. The long-term effects and optimal dosages are still being investigated, and individual responses can vary. Additionally, the supplementation should not be viewed as a standalone solution but rather as part of a comprehensive approach to lung health that includes lifestyle modifications, proper nutrition, and medical guidance.
For those considering glutathione supplementation to support lung function, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice based on individual health status, potential interactions with other medications, and the most appropriate form of supplementation if deemed necessary.
Conclusion
The connection between glutathione and healthy lung function is a fascinating area of ongoing research. As we continue to uncover the intricate ways in which this powerful antioxidant supports respiratory health, it becomes increasingly clear that maintaining optimal glutathione levels is crucial for lung function and overall well-being.
While supplementation may offer potential benefits, it's important to remember that a holistic approach to lung health is key. This includes adopting a healthy lifestyle, avoiding environmental toxins when possible, and working closely with healthcare providers to address any respiratory concerns.
For those interested in learning more about glutathione and its potential benefits for lung health, or exploring high-quality supplements, we invite you to reach out to us at info@yanggebiotech.com. Our team of experts is dedicated to providing innovative, natural solutions to support your health and wellness journey.
References
1. Rahman, I., & MacNee, W. (2000). Oxidative stress and regulation of glutathione in lung inflammation. European Respiratory Journal, 16(3), 534-554.
2. Cantin, A. M., & Begin, R. (1991). Glutathione and inflammatory disorders of the lung. Lung, 169(1), 123-138.
3. Ghezzi, P. (2011). Role of glutathione in immunity and inflammation in the lung. International Journal of General Medicine, 4, 105-113.
4. Visca, A., Bishop, C. T., Hilton, S. C., & Hudson, V. M. (2008). Improvement in clinical markers in CF patients using a reduced glutathione regimen: An uncontrolled, observational study. Journal of Cystic Fibrosis, 7(5), 433-436.
5. Behr, J., Degenkolb, B., Krombach, F., & Vogelmeier, C. (2002). Intracellular glutathione and bronchoalveolar cells in fibrosing alveolitis: effects of N-acetylcysteine. European Respiratory Journal, 19(5), 906-911.

Based on your location and order quantity, you will have the opportunity to receive a limited time free shipping promotion!

Who we are


