Phycocyanin Spirulina: Sustainable Protein for a Growing World
As the global population continues to expand, finding sustainable sources of protein to nourish billions of people has become one of the most pressing challenges of our time. Enter phycocyanin spirulina - a nutrient-dense, eco-friendly "superfood" that may play a key role in feeding the world in the coming decades. This vibrant blue-green algae is packed with high-quality protein, essential vitamins and minerals, and powerful antioxidants. Its cultivation requires minimal resources compared to traditional livestock farming, making it an environmentally sustainable option for meeting the world's growing protein needs.

Health benefits of phycocyanin spirulina protein
Phycocyanin spirulina offers an impressive array of evidence-based health benefits, thanks to its unique nutritional profile and bioactive compounds. Let's take a closer look at some of the key ways this superfood algae can support overall health and wellbeing:
Nutrient-dense complete protein
One of the most remarkable attributes of phycocyanin spirulina is its exceptional protein content and quality. This blue-green algae contains up to 70% protein by dry weight, surpassing most plant-based protein sources. More importantly, it's considered a complete protein, containing all nine essential amino acids in balanced proportions. This makes phycocyanin spirulina an excellent protein option for vegetarians, vegans, and anyone looking to diversify their protein sources.
The high-quality protein in phycocyanin spirulina supports muscle growth and repair, immune function, and the production of enzymes and hormones. Its easy digestibility and bioavailability mean the body can efficiently utilize the protein for various physiological processes. For athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and those recovering from illness or injury, phycocyanin spirulina provides a valuable source of readily absorbable protein to support recovery and overall health.
Powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects
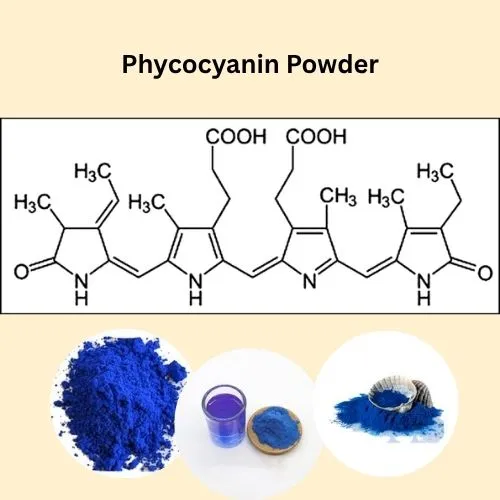
Phycocyanin, the pigment-protein complex that gives spirulina its distinctive blue color, is a potent antioxidant with remarkable anti-inflammatory properties. Research has shown that phycocyanin can neutralize harmful free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in the body. This antioxidant activity may help protect cells from damage and lower the risk of chronic diseases associated with inflammation and oxidative stress.
Studies have demonstrated that phycocyanin may be particularly effective in reducing inflammation markers in the body. This anti-inflammatory action could have wide-ranging benefits, from supporting joint health to potentially lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease and certain types of cancer. The antioxidant prowess of phycocyanin spirulina makes it a valuable addition to any diet focused on promoting longevity and overall wellness.
Cardiovascular health support
Emerging research suggests that phycocyanin spirulina may offer significant benefits for heart health. Several studies have shown that regular consumption of spirulina can help lower total cholesterol, reduce "bad" LDL cholesterol, and increase "good" HDL cholesterol levels. These effects on lipid profiles could translate to a reduced risk of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases.
Additionally, phycocyanin spirulina has been found to have potential blood pressure-lowering effects. The nitric oxide-boosting properties of spirulina may help relax blood vessels, improving circulation and potentially reducing hypertension. For individuals looking to support their cardiovascular health through natural means, incorporating phycocyanin spirulina into their diet could be a beneficial strategy.

Innovative uses of phycocyanin spirulina in foods
Beyond its use as a dietary supplement, phycocyanin spirulina is making waves in the food industry as an innovative ingredient with multiple applications. Its unique properties are opening up exciting possibilities for creating healthier, more visually appealing, and sustainable food products.
Natural blue food coloring
One of the most promising applications of phycocyanin spirulina is as a natural blue food coloring. In an era where consumers are increasingly wary of artificial additives, food manufacturers are seeking natural alternatives to synthetic food dyes. Phycocyanin's vibrant blue hue provides an excellent solution, offering a clean-label option for coloring various food and beverage products.
The stability and intensity of phycocyanin's blue color make it suitable for use in a wide range of applications, from confectionery and baked goods to dairy products and beverages. Unlike some other natural blue colorants, phycocyanin maintains its color well under various pH conditions and processing methods. This versatility has led to its increasing adoption in the food industry as a natural, eye-catching coloring agent.
Protein fortification in plant-based products
As the plant-based food market continues to expand, manufacturers are constantly seeking ways to improve the nutritional profiles of their products. Phycocyanin spirulina offers an excellent solution for protein fortification in plant-based alternatives to meat, dairy, and egg products. Its complete amino acid profile can help bridge nutritional gaps often found in purely plant-based diets.
Innovative food companies are incorporating phycocyanin spirulina into products like plant-based burgers, non-dairy yogurts, and vegan protein powders. Not only does this boost the protein content of these products, but it also adds valuable micronutrients and antioxidants. The neutral taste of phycocyanin spirulina allows for its incorporation without significantly altering the flavor profile of the end product.
Functional beverages and smoothie bowls
The rise of functional beverages and Instagram-worthy smoothie bowls has created new opportunities for phycocyanin spirulina in the food and beverage industry. Health-conscious consumers are increasingly seeking out beverages and foods that not only taste good but also provide tangible health benefits. Phycocyanin spirulina fits perfectly into this trend, offering a nutrient-dense boost to smoothies, juices, and other functional beverages.
Innovative beverage companies are creating blue spirulina lattes, antioxidant-rich smoothie blends, and energizing sports drinks featuring phycocyanin spirulina. In the realm of smoothie bowls, the vivid blue color of phycocyanin creates visually stunning creations that are as nutritious as they are beautiful. These applications not only capitalize on the health benefits of phycocyanin spirulina but also tap into the growing consumer desire for natural, functional ingredients in their daily diets.

Sustainability trends in phycocyanin spirulina farming
As the demand for phycocyanin spirulina continues to grow, so does the focus on sustainable cultivation practices. The algae's inherent environmental benefits, combined with innovative farming techniques, are positioning phycocyanin spirulina as a key player in sustainable food production.
Water-efficient cultivation methods
One of the most significant advantages of phycocyanin spirulina cultivation is its remarkably low water footprint compared to traditional protein sources. Spirulina can be grown in shallow ponds or bioreactors, requiring far less water than livestock farming or even many plant-based protein crops. Advanced cultivation systems are further improving water efficiency through recirculation and filtration techniques.
Innovative aquaculture systems are being developed that integrate spirulina cultivation with other forms of agriculture, creating closed-loop systems that maximize water use efficiency. These systems not only conserve water but also minimize nutrient runoff, reducing the environmental impact of spirulina production. As water scarcity becomes an increasingly pressing global issue, the water-efficient nature of spirulina cultivation positions it as a sustainable protein source for the future.
Carbon sequestration potential
Phycocyanin spirulina cultivation offers exciting possibilities for carbon sequestration, potentially playing a role in mitigating climate change. Like all photosynthetic organisms, spirulina absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere as it grows. However, spirulina's rapid growth rate and high biomass yield mean it can sequester carbon more efficiently than many terrestrial plants.
Research is ongoing into optimizing spirulina cultivation for maximum carbon capture. Some innovative projects are exploring the use of spirulina farms to absorb carbon dioxide emissions from industrial processes, creating a win-win situation for both food production and environmental protection. As the world seeks solutions to reduce atmospheric carbon levels, the carbon sequestration potential of phycocyanin spirulina farming could become an increasingly valuable asset.
Vertical farming and urban cultivation
The compact nature of spirulina cultivation makes it well-suited for vertical farming and urban agriculture initiatives. Unlike traditional crops that require extensive land area, spirulina can be grown in stacked bioreactors or even on rooftops, maximizing space efficiency in urban environments. This opens up possibilities for local, sustainable protein production in cities, reducing transportation costs and carbon emissions associated with food distribution.
Innovative urban farming projects are already incorporating spirulina cultivation into their operations. These initiatives not only produce nutritious food but also serve as educational tools, raising awareness about sustainable agriculture and nutrition. As cities grapple with food security issues and seek to reduce their environmental footprint, urban spirulina cultivation could become an increasingly common sight, bringing food production closer to consumers and creating new green spaces in urban areas.
Conclusion
Phycocyanin spirulina stands out as a remarkable superfood with immense potential to address global nutrition and sustainability challenges. Its exceptional protein content, powerful health benefits, and versatile applications in the food industry make it a valuable resource for improving diets worldwide. The sustainable cultivation practices associated with spirulina farming further underscore its importance in creating a more environmentally friendly food system. As research continues and innovation in cultivation and application methods advances, phycocyanin spirulina is poised to play an increasingly significant role in nourishing a growing world population while minimizing environmental impact.
Are you interested in harnessing the power of phycocyanin spirulina for your food, beverage, or supplement products? Yangge Biotech Co., Ltd. is at the forefront of natural plant extract innovation, offering high-quality phycocyanin spirulina and a wide range of other botanical ingredients. Our ISO, HACCP, Kosher, and Halal certified products are backed by rigorous quality control and a commitment to sustainability. Whether you're developing functional foods, natural colorants, or nutritional supplements, we have the expertise and products to support your needs. Contact us at info@yanggebiotech.com to explore how our phycocyanin spirulina can elevate your offerings and contribute to a healthier, more sustainable future.
FAQ
Q: Can we get some samples to test before purchasing?
A: Of course, we can provide free samples of 20 to 100 grams, but the shipping cost is at the customer's expense. The shipping cost can be deducted from the next order, or the samples can be sent through your courier account.
Q: Do your products have relevant certifications?
A: Yes, our products are certified for HALAL, ISO, HACCP, Kosher, and other certifications.
Q: What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ)?
A: Small batches of samples can be customized according to your requirements.
Q: Do you offer OEM and ODM services? Can the formula be customized based on our own?
A: Of course, we provide ODM and OEM services to many customers. Our product range includes softgels, capsules, tablets, sachets, granules, and private label services. Simply contact us and let us know your requirements. Our experienced R&D team can also develop new products with specific formulas.
Please contact us to design your own branded products.
Q: How do you handle quality complaints?
A: First, we have a comprehensive quality control SOP. We provide authoritative third-party inspection reports for almost all products before shipment to minimize the possibility of quality issues. Second, we have a comprehensive return and exchange procedure. If there is a genuine quality dispute, we will strictly follow the SOP.
Q: How do you ship? How long does delivery take?
A: For small orders, we typically use DHL, UPS, EMS, FedEx, or TNT. Delivery typically takes 3-7 days. We also offer air and sea freight services. We have a strong freight forwarding team and can provide you with a one-stop service, including DDP and DDU.
Q: What are your payment terms?
A: 100% prepayment, payable by T/T, Western Union, MoneyGram, or PayPal.
Q: What is the shelf life of your products?
A: 2 years with proper storage.
Q: Is the packaging environmentally friendly?
A: We attach great importance to environmental protection and are constantly improving our product packaging. Some products are packaged in recyclable paper. Packaging materials are carefully selected to ensure product safety during transportation and storage, and to minimize environmental impact. We are committed to achieving a balance between environmental friendliness and practicality in our product packaging, and to contributing to sustainable development.
References
1. Johnson, E. M., & Kumar, S. (2021). Phycocyanin: A Promising Compound for Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 61(12), 1920-1933.
2. Martínez-Galero, E., et al. (2020). Spirulina maxima and Its Protein Extract Protect against Hydroxyurea-Teratogenic Insult in Mice. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 136, 111025.
3. Pagels, F., et al. (2019). Phycobiliproteins: Potential and Challenges in Food, Health and Cosmetic Industries. Algal Research, 41, 101559.
4. Soni, R. A., Sudhakar, K., & Rana, R. S. (2017). Spirulina – From Growth to Nutritional Product: A Review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 69, 157-171.
5. Wu, Q., et al. (2016). The Antioxidant, Immunomodulatory, and Anti-inflammatory Activities of Spirulina: An Overview. Archives of Toxicology, 90(8), 1817-1840.

Based on your location and order quantity, you will have the opportunity to receive a limited time free shipping promotion!

Who we are


