Melatonin and Jet Lag: A Traveler’s Best Friend
Frequent travelers know the struggle of adjusting to new time zones all too well. Jet lag can turn an exciting trip into a groggy, disorienting experience. But what if there was a natural way to help your body adapt more quickly? Enter melatonin, a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating our sleep-wake cycles. This article explores how melatonin can be a traveler's secret weapon against jet lag.
How Melatonin Can Help Reduce Jet Lag?
Jet lag happens when our internal body clock is not aligned with the local time at our destination, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, insomnia, and trouble focusing. This disruption can make it challenging to adjust to a new time zone. Melatonin, commonly known as the "sleep hormone," plays a crucial role in regulating our circadian rhythm. By supplementing with melatonin, it can help reset the body’s internal clock, easing the transition and improving sleep quality during travel.
Our bodies naturally produce melatonin in response to darkness, signaling that it's time to sleep. However, when we cross time zones, this natural production can be disrupted. Supplementing with melatonin can help trick your body into adjusting to the new schedule more rapidly. Research has shown that melatonin can be particularly effective for eastward travel, which tends to cause more severe jet lag symptoms. By taking melatonin at the appropriate time, travelers can potentially reduce the duration and intensity of jet lag, allowing them to enjoy their destination sooner.
Melatonin Usage Tips for Long Flights
To maximize the benefits of melatonin for combating jet lag, consider the following tips:
- Timing is Crucial: Take melatonin close to your target bedtime at the destination. This helps to shift your internal body clock and align it with the local time zone, easing the adjustment to your new schedule.
- Start Before Your Trip: Begin taking melatonin a few days prior to departure to give your body a head start on adjusting. By gradually introducing melatonin, you can help your body prepare for the time zone change and reduce the severity of jet lag symptoms once you arrive at your destination.
- Choose the Right Dosage: Most studies suggest a melatonin dose between 0.5 to 5 mg for jet lag relief. Start with a lower dose, such as 0.5 mg or 1 mg, to gauge your body’s response, and adjust as needed. Higher doses may not necessarily be more effective and can sometimes cause unwanted side effects.
- Consider Slow-Release Formulations: Slow-release melatonin formulations can help maintain steady melatonin levels throughout the night, offering a more sustained effect compared to regular melatonin supplements.
- Combine with Light Exposure: Exposure to natural light at the right times can complement melatonin and enhance its ability to reset your body clock. In the morning, exposure to sunlight can help advance your circadian rhythm, while evening light exposure can delay it.
Remember, melatonin is just one tool in your jet lag-fighting arsenal. Hydration, proper nutrition, and strategic napping can also play important roles in helping you adjust to new time zones.

Precautions When Using Melatonin While Traveling
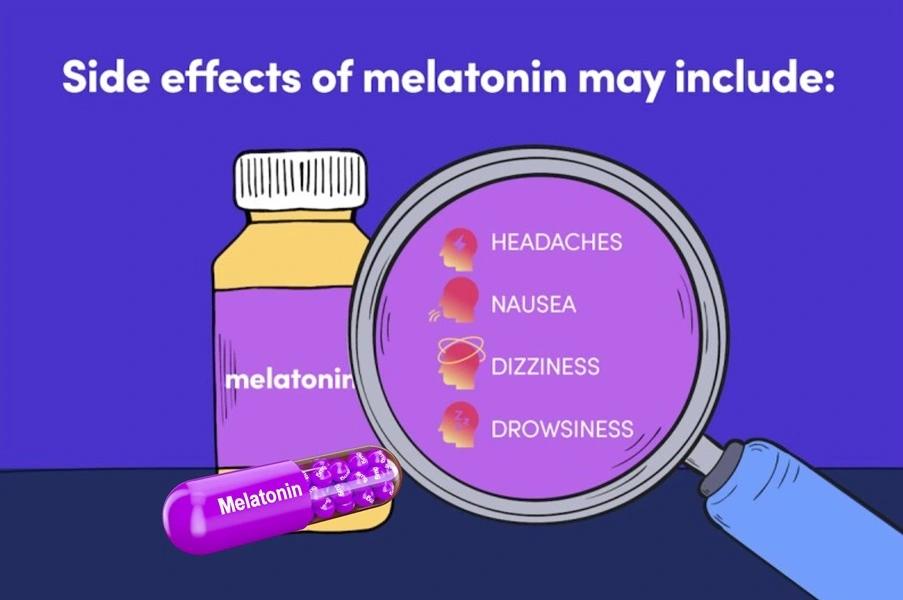
While melatonin is generally considered safe for short-term use, it's important to be aware of potential side effects and interactions:
- Drowsiness: Melatonin can induce drowsiness, making it essential to avoid activities that require full alertness, such as driving or operating machinery, after taking the supplement. Since it affects your sleep-wake cycle, it’s best to take it when you’re preparing for sleep and can rest afterward.
- Potential Interactions: Melatonin can interact with certain medications, including blood thinners, immunosuppressants, and others that affect the central nervous system. If you're taking prescription or over-the-counter medications, it’s crucial to consult with your healthcare provider before using melatonin. They can help determine if melatonin is safe for you and ensure that it doesn’t interfere with your medications.
- Timing is Key: The timing of melatonin intake is crucial to its effectiveness. Taking melatonin at the wrong time, such as too early or too late, can actually worsen jet lag symptoms instead of improving them. Always follow the recommended timing guidelines based on your travel direction and destination's time zone. For instance, if you're traveling east, taking melatonin in the evening can help you adjust to an earlier bedtime.
- Quality Matters: Not all melatonin supplements are created equal. To ensure that you are getting a product that is both pure and potent, it’s important to choose a reputable brand. Look for brands that are transparent about ingredient sourcing and have good manufacturing practices. Reading product reviews and checking for third-party testing can help you make an informed decision.
- Individual Differences: Everyone’s body responds differently to melatonin. While it’s generally considered safe for most people, some may be more sensitive to its effects. It’s a good idea to start with a lower dose, such as 0.5 mg or 1 mg, to gauge your body’s response and assess your tolerance. You can gradually adjust the dose based on how you feel, but always start low to minimize the risk of unwanted side effects.
Conclusion
Melatonin can be a valuable ally in the battle against jet lag, helping travelers adjust more quickly to new time zones and enjoy their destinations to the fullest. By understanding how to use melatonin effectively and safely, you can potentially reduce the impact of jet lag on your travel experiences. Remember, while melatonin can be beneficial, it's not a magic solution. Combining melatonin use with other jet lag mitigation strategies, such as gradually adjusting your sleep schedule before travel and staying hydrated, can yield the best results.
For high-quality melatonin raw powder and other natural plant extracts, Yangge Biotech Co., Ltd. offers innovative solutions for dietary supplements and more. To learn about our range of products, please contact us at info@yanggebiotech.com.
FAQ
Q: Can we get some samples to test before purchasing?
A: Of course, we can provide free samples of 20 to 100 grams, but the shipping cost is at the customer's expense. The shipping cost can be deducted from the next order, or the samples can be sent through your courier account.
Q: Do your products have relevant certifications?
A: Yes, our products are certified for HALAL, ISO, HACCP, Kosher, and other certifications.
Q: What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ)?
A: Small batches of samples can be customized according to your requirements.
Q: Do you offer OEM and ODM services? Can the formula be customized based on our own?
A: Of course, we provide ODM and OEM services to many customers. Our product range includes softgels, capsules, tablets, sachets, granules, and private label services. Simply contact us and let us know your requirements. Our experienced R&D team can also develop new products with specific formulas.
Please contact us to design your own branded products.
Q: How do you handle quality complaints?
A: First, we have a comprehensive quality control SOP. We provide authoritative third-party inspection reports for almost all products before shipment to minimize the possibility of quality issues. Second, we have a comprehensive return and exchange procedure. If there is a genuine quality dispute, we will strictly follow the SOP.
Q: How do you ship? How long does delivery take?
A: For small orders, we typically use DHL, UPS, EMS, FedEx, or TNT. Delivery typically takes 3-7 days. We also offer air and sea freight services. We have a strong freight forwarding team and can provide you with a one-stop service, including DDP and DDU.
Q: What are your payment terms?
A: 100% prepayment, payable by T/T, Western Union, MoneyGram, or PayPal.
Q: What is the shelf life of your products?
A: 2 years with proper storage.
Q: Is the packaging environmentally friendly?
A: We attach great importance to environmental protection and are constantly improving our product packaging. Some products are packaged in recyclable paper. Packaging materials are carefully selected to ensure product safety during transportation and storage, and to minimize environmental impact. We are committed to achieving a balance between environmental friendliness and practicality in our product packaging, and to contributing to sustainable development.
References
1. Herxheimer, A., & Petrie, K. J. (2002). Melatonin for the prevention and treatment of jet lag. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (2).
2. Arendt, J. (2019). Melatonin: Countering chaotic time cues. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 45, 127-135.
3. Eastman, C. I., & Burgess, H. J. (2009). How to travel the world without jet lag. Sleep Medicine Clinics, 4(2), 241-255.
4. Waterhouse, J., Reilly, T., & Edwards, B. (2007). Jet lag: trends and coping strategies. The Lancet, 369(9567), 1117-1129.
5. Sack, R. L. (2010). Jet lag. New England Journal of Medicine, 362(5), 440-447.

Based on your location and order quantity, you will have the opportunity to receive a limited time free shipping promotion!

Who we are


