Is Almond Protein Good for Digestion and Allergies?
Almond protein has gained popularity as a plant-based protein source, but many people wonder about its effects on digestion and allergies. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the benefits of almond protein for gut health, its potential impact on common allergies, and how it compares to other plant-based proteins. Whether you're considering incorporating almond protein into your diet or simply curious about its health benefits, this article will provide valuable insights to help you make informed decisions.

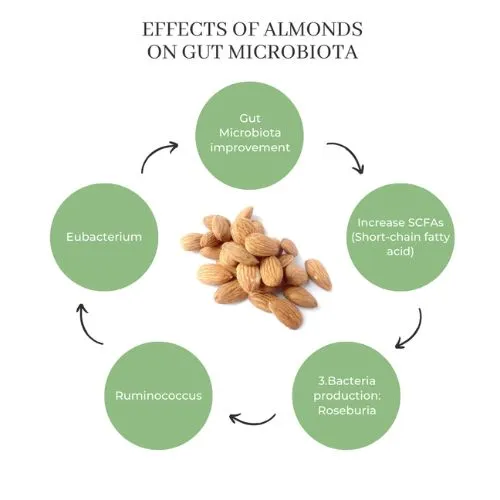
How Almond Protein Improves Gut Health and Digestion?
Almond protein offers several benefits for digestive health, making it an excellent choice for those looking to improve their gut function. Let's delve into the ways almond protein can positively impact your digestive system:
Fiber-Rich Protein Source
One of the key advantages of almond protein is its high fiber content. Fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy digestive system by promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. The combination of protein and fiber in almonds helps slow down digestion, leading to a gradual release of nutrients and improved satiety.
Prebiotic Properties
Almond protein contains prebiotic compounds that serve as food for beneficial gut bacteria. These prebiotics help nourish and support the growth of probiotics in your digestive tract, contributing to a balanced gut microbiome. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for proper digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall immune function.
Enzyme Support
Almonds are a rich source of enzymes that aid in the breakdown of nutrients. When consumed as almond protein powder, these enzymes can help improve the digestion and absorption of other nutrients in your diet. This enzymatic support can be particularly beneficial for individuals with compromised digestive systems or those looking to optimize their nutrient intake.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Almond protein contains various antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds that can help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract. By mitigating inflammation, almond protein may alleviate symptoms associated with digestive disorders and promote overall gut health.
Can Almond Protein Help with Common Allergies?
While almonds themselves can be an allergen for some individuals, almond protein may have potential benefits for managing certain allergies. Here's what you need to know about almond protein and allergies:
Hypoallergenic Alternative
For individuals with allergies to common protein sources like dairy or soy, almond protein can serve as a hypoallergenic alternative. It provides a plant-based protein option that is less likely to trigger allergic reactions in those who are not sensitive to tree nuts.
Potential Anti-Allergic Properties
Some studies suggest that almonds may have anti-allergic properties due to their high vitamin E content and other antioxidants. These compounds could potentially help reduce the severity of allergic reactions by modulating the immune response. However, more research is needed to fully understand the extent of these benefits.
Nut Allergy Considerations
It's important to note that individuals with tree nut allergies should exercise caution when considering almond protein. While some people with nut allergies may tolerate almonds, others may experience severe allergic reactions. Always consult with a healthcare professional before introducing almond protein into your diet if you have a history of nut allergies.
Cross-Reactivity
In some cases, individuals allergic to birch pollen may experience cross-reactivity with almonds. This phenomenon, known as oral allergy syndrome, can cause mild symptoms such as itching or tingling in the mouth. If you have a birch pollen allergy, it's advisable to discuss the use of almond protein with your allergist.

Almond Protein vs. Other Plant-Based Proteins for Health
When comparing almond protein to other plant-based protein sources, it's essential to consider various factors that contribute to overall health. Let's examine how almond protein stacks up against other popular plant-based proteins:
Nutritional Profile
Almond protein boasts a well-rounded nutritional profile, offering not only protein but also healthy fats, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Compared to some other plant-based proteins, almond protein provides a more comprehensive array of nutrients, making it an excellent choice for those seeking a balanced protein source.
Amino Acid Composition
While almond flavor protein contains all nine essential amino acids, it is not considered a complete protein due to its lower levels of lysine. However, when combined with other plant-based proteins like legumes or grains, almond protein can contribute to a complete amino acid profile. This versatility allows for easy incorporation into various dietary patterns.
Digestibility
Almond protein is generally well-tolerated and easily digestible for most individuals. Its digestibility score is comparable to other plant-based proteins like pea or rice protein. The presence of enzymes in almonds may even enhance the overall digestibility of meals containing almond protein.
Allergen Considerations
Compared to soy or wheat protein, almond protein may be a suitable alternative for individuals with common food allergies. However, it's important to remember that almonds are still a potential allergen for some people, particularly those with tree nut allergies.
Environmental Impact
When considering the environmental aspect, almond protein has a lower carbon footprint compared to animal-based proteins. However, almond cultivation does require significant water resources. Other plant-based proteins like pea or hemp protein may have a lower environmental impact in terms of water usage.
Versatility in Cooking
Almond protein offers a mild, nutty flavor that blends well in various recipes. Its versatility makes it an excellent choice for baking, smoothies, and other culinary applications. Some other plant-based proteins may have stronger flavors or textures that limit their use in certain dishes.

Conclusion
In conclusion, almond protein offers numerous benefits for digestion and overall health. Its fiber content, prebiotic properties, and potential anti-inflammatory effects make it a valuable addition to a balanced diet. While it may help manage certain allergies, individuals with nut allergies should exercise caution. When compared to other plant-based proteins, almond protein stands out for its nutritional profile and versatility.
If you're interested in incorporating almond protein into your diet or learning more about plant-based protein options, don't hesitate to contact us at info@yanggebiotech.com. Our team of experts is ready to assist you in finding the perfect protein solution for your needs.
FAQ
Q: Can we get some samples to test before purchasing?
A: Of course, we can provide free samples of 20 to 100 grams, but the shipping cost is at the customer's expense. The shipping cost can be deducted from the next order, or the samples can be sent through your courier account.
Q: Do your products have relevant certifications?
A: Yes, our products are certified for HALAL, ISO, HACCP, Kosher, and other certifications.
Q: What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ)?
A: Small batches of samples can be customized according to your requirements.
Q: Do you offer OEM and ODM services? Can the formula be customized based on our own?
A: Of course, we provide ODM and OEM services to many customers. Our product range includes softgels, capsules, tablets, sachets, granules, and private label services. Simply contact us and let us know your requirements. Our experienced R&D team can also develop new products with specific formulas.
Please contact us to design your own branded products.
Q: How do you handle quality complaints?
A: First, we have a comprehensive quality control SOP. We provide authoritative third-party inspection reports for almost all products before shipment to minimize the possibility of quality issues. Second, we have a comprehensive return and exchange procedure. If there is a genuine quality dispute, we will strictly follow the SOP.
Q: How do you ship? How long does delivery take?
A: For small orders, we typically use DHL, UPS, EMS, FedEx, or TNT. Delivery typically takes 3-7 days. We also offer air and sea freight services. We have a strong freight forwarding team and can provide you with a one-stop service, including DDP and DDU.
Q: What are your payment terms?
A: 100% prepayment, payable by T/T, Western Union, MoneyGram, or PayPal.
Q: What is the shelf life of your products?
A: 2 years with proper storage.
Q: Is the packaging environmentally friendly?
A: We attach great importance to environmental protection and are constantly improving our product packaging. Some products are packaged in recyclable paper. Packaging materials are carefully selected to ensure product safety during transportation and storage, and to minimize environmental impact. We are committed to achieving a balance between environmental friendliness and practicality in our product packaging, and to contributing to sustainable development.
References
1. Holscher, H. D., et al. (2018). Almond Consumption and Processing Affects the Composition of the Gastrointestinal Microbiota of Healthy Adult Men and Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 10(2), 126.
2. Mandalari, G., et al. (2008). Release of protein, lipid, and vitamin E from almond seeds during digestion. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56(9), 3409-3416.
3. Crespo, J. F., et al. (2006). Frequency of food allergy in a pediatric population from Spain. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology, 17(5), 356-363.
4. Kamil, A., & Chen, C. Y. (2012). Health benefits of almonds beyond cholesterol reduction. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 60(27), 6694-6702.
5. Ros, E. (2010). Health benefits of nut consumption. Nutrients, 2(7), 652-682.

Based on your location and order quantity, you will have the opportunity to receive a limited time free shipping promotion!

Who we are


