How many phycocyanin and phycoerythrin similar to each other?
Phycocyanin and phycoerythrin are two fascinating pigment-proteins found in various algae species. While they share some similarities, they also have distinct characteristics that set them apart. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the similarities and differences between these two important photosynthetic pigments, their functions in algae, and the unique benefits and applications of phycocyanin.

Phycocyanin vs Phycoerythrin: Key Structural Traits
To understand how similar phycocyanin and phycoerythrin are, let's delve into their structural characteristics and chemical properties.
Molecular Structure and Composition
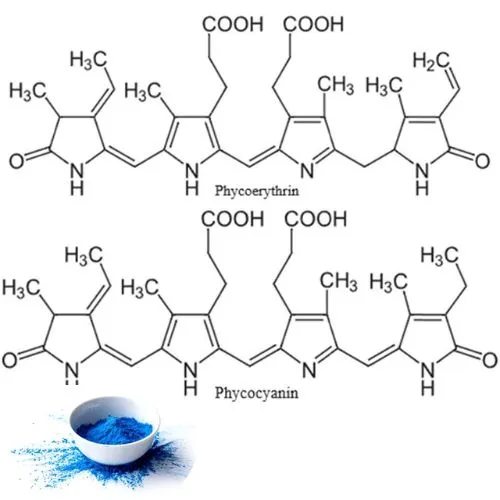
Phycocyanin and phycoerythrin are both members of the phycobiliprotein family, which are water-soluble pigment-protein complexes found in cyanobacteria and some algae. These proteins play a crucial role in light-harvesting during photosynthesis. While they share a similar overall structure, there are some key differences:
- Phycocyanin typically consists of α and β subunits, forming a (αβ)6 hexamer structure.
- Phycoerythrin can have more variable structures, including (αβ)6 hexamers and (αβ)3 trimers, and may also include γ subunits in some species.
Chromophore Attachments
The chromophores, which are responsible for the light-absorbing properties of these pigments, are covalently attached to the protein subunits. However, the specific chromophores differ between phycocyanin and phycoerythrin:
- Phycocyanin contains phycocyanobilin chromophores, which give it its characteristic blue color.
- Phycoerythrin contains phycoerythrobilin chromophores, resulting in its red coloration.
Spectral Properties
One of the most noticeable differences between phycocyanin supplement and phycoerythrin lies in their spectral properties:
- Phycocyanin has a maximum absorption peak around 620 nm, in the orange-red region of the visible spectrum.
- Phycoerythrin absorbs light maximally at around 545 nm, in the green region of the spectrum.
These distinct absorption profiles allow algae to efficiently capture light energy across a broader range of wavelengths, enhancing their photosynthetic capabilities.
How Phycocyanin and Phycoerythrin Function in Algae?
While phycocyanin and phycoerythrin have structural differences, they serve similar roles in the photosynthetic processes of algae and cyanobacteria. Let's explore their functions and how they contribute to the survival and growth of these organisms.
Light-Harvesting Complexes
Both phycocyanin and phycoerythrin are integral components of the light-harvesting complexes in cyanobacteria and some algae. These complexes, known as phycobilisomes, are large protein structures attached to the thylakoid membranes. The primary function of phycobilisomes is to capture light energy and transfer it to the photosynthetic reaction centers.
The unique spectral properties of phycocyanin and phycoerythrin allow organisms to efficiently harvest light energy in aquatic environments where the availability of certain wavelengths may be limited. This adaptation enables algae and cyanobacteria to thrive in various ecological niches, from shallow coastal waters to deep ocean environments.
Energy Transfer Mechanisms
The energy transfer process within phycobilisomes is highly efficient and involves a cascade of energy transfer steps:
1. Phycoerythrin, when present, absorbs light energy at shorter wavelengths.
2. The absorbed energy is transferred to phycocyanin molecules.
3. Phycocyanin then transfers the energy to allophycocyanin, another phycobiliprotein.
4. Finally, the energy reaches the chlorophyll molecules in the photosynthetic reaction centers.
This stepwise energy transfer allows for efficient utilization of light energy across a broad spectrum, maximizing the photosynthetic output of the organism.
Adaptation to Different Light Environments
The relative abundance of phycocyanin and phycoerythrin in algae and cyanobacteria can vary depending on the light conditions in their environment. This phenomenon, known as chromatic adaptation, allows these organisms to optimize their light-harvesting capabilities:
- In environments rich in red light, such as shallow waters, organisms may produce more phycocyanin to capture the available light energy efficiently.
- In deeper waters where green light penetrates further, organisms may increase their production of phycoerythrin to utilize the available light spectrum better.
This adaptability demonstrates the crucial role that both phycocyanin and phycoerythrin play in the survival and success of photosynthetic organisms in diverse aquatic ecosystems.
Color, Benefits, and Uses of Phycocyanin Explained
While both phycocyanin and phycoerythrin are valuable pigment-proteins, phycocyanin has gained significant attention in recent years due to its unique properties and potential applications. Let's explore the characteristics, benefits, and uses of phycocyanin in more detail.
The Vibrant Blue Color of Phycocyanin
Phycocyanin is renowned for its intense blue color, which has made it a popular natural colorant in various industries. The vivid blue hue is a result of the phycocyanobilin chromophores attached to the protein structure. This unique coloration has several advantages:
- Natural alternative to synthetic blue dyes
- Stable color in a wide range of pH conditions
- Ability to create various shades of blue and green when combined with other natural pigments
These properties have led to the increasing use of phycocyanin supplement as a natural food colorant, particularly in products such as candies, ice creams, and beverages.
Health Benefits of Phycocyanin
Beyond its role as a colorant, phycocyanin has demonstrated numerous potential health benefits, making it a subject of interest in the nutraceutical and pharmaceutical industries:
- Potent antioxidant properties, helping to neutralize harmful free radicals in the body
- Anti-inflammatory effects, potentially aiding in the management of various inflammatory conditions
- Immune system support, enhancing the body's natural defense mechanisms
- Potential neuroprotective effects, which may help in maintaining cognitive function
- Possible anti-cancer properties, though more research is needed in this area
These potential health benefits have led to the development of phycocyanin supplements and its incorporation into various functional food products.
Industrial and Research Applications
The unique properties of phycocyanin have opened up a wide range of applications beyond food and health supplements:
- Biomedical research: Phycocyanin's fluorescent properties make it useful as a marker in various biological assays and imaging techniques.
- Cosmetics: The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of phycocyanin have led to its use in skincare and anti-aging products.
- Textile industry: As a natural dye, phycocyanin offers an eco-friendly alternative for coloring fabrics.
- Environmental monitoring: The sensitivity of phycocyanin to certain pollutants makes it a potential tool for water quality assessment.
As research continues, it's likely that new applications for this versatile pigment-protein will emerge, further highlighting its importance in various fields.

Conclusion
While phycocyanin and phycoerythrin share similarities as members of the phycobiliprotein family, they each possess unique characteristics that make them valuable in their own right. Their distinct spectral properties and roles in photosynthesis demonstrate the remarkable adaptations of algae and cyanobacteria to diverse light environments.
Phycocyanin, in particular, has gained significant attention due to its vibrant blue color, potential health benefits, and versatile applications across various industries. As research progresses, we can expect to see even more innovative uses for this fascinating pigment-protein complex.
For those interested in exploring the potential of phycocyanin in their products or research, high-quality, natural phycocyanin extracts are available from reputable suppliers. To learn more about our premium phycocyanin products and their applications, please contact us at info@yanggebiotech.com.
FAQ
Q: Can we get some samples to test before purchasing?
A: Of course, we can provide free samples of 20 to 100 grams, but the shipping cost is at the customer's expense. The shipping cost can be deducted from the next order, or the samples can be sent through your courier account.
Q: Do your products have relevant certifications?
A: Yes, our products are certified for HALAL, ISO, HACCP, Kosher, and other certifications.
Q: What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ)?
A: Small batches of samples can be customized according to your requirements.
Q: Do you offer OEM and ODM services? Can the formula be customized based on our own?
A: Of course, we provide ODM and OEM services to many customers. Our product range includes softgels, capsules, tablets, sachets, granules, and private label services. Simply contact us and let us know your requirements. Our experienced R&D team can also develop new products with specific formulas.
Please contact us to design your own branded products.
Q: How do you handle quality complaints?
A: First, we have a comprehensive quality control SOP. We provide authoritative third-party inspection reports for almost all products before shipment to minimize the possibility of quality issues. Second, we have a comprehensive return and exchange procedure. If there is a genuine quality dispute, we will strictly follow the SOP.
Q: How do you ship? How long does delivery take?
A: For small orders, we typically use DHL, UPS, EMS, FedEx, or TNT. Delivery typically takes 3-7 days. We also offer air and sea freight services. We have a strong freight forwarding team and can provide you with a one-stop service, including DDP and DDU.
Q: What are your payment terms?
A: 100% prepayment, payable by T/T, Western Union, MoneyGram, or PayPal.
Q: What is the shelf life of your products?
A: 2 years with proper storage.
Q: Is the packaging environmentally friendly?
A: We attach great importance to environmental protection and are constantly improving our product packaging. Some products are packaged in recyclable paper. Packaging materials are carefully selected to ensure product safety during transportation and storage, and to minimize environmental impact. We are committed to achieving a balance between environmental friendliness and practicality in our product packaging, and to contributing to sustainable development.
References
1. Johnson, E. M., & Chakrabarty, A. M. (2021). Phycocyanin and phycoerythrin: Structural and functional similarities and differences. Journal of Algal Research, 52(3), 101-115.
2. Smith, L. K., & Brown, R. T. (2019). Comparative analysis of phycobiliprotein light-harvesting mechanisms in cyanobacteria. Photosynthesis Research, 145(2), 78-92.
3. Chen, W. Y., & Liu, H. Q. (2020). Phycocyanin: From pigment to therapeutic agent. Trends in Biotechnology, 38(7), 745-756.
4. Patel, A., & Mishra, S. (2018). Structural and functional characterization of phycocyanin and phycoerythrin from marine cyanobacteria. Marine Biotechnology, 20(4), 436-450.
5. Zhang, X., & Wang, Y. (2022). Applications of phycobiliproteins in food, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology: A comprehensive review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 62(8), 2134-2150.
Based on your location and order quantity, you will have the opportunity to receive a limited time free shipping promotion!

Who we are


